Now that we know what to expect to see when we look at the sky, the next thing to learn is where to look and when to look.
There are a lot of software available online which plot the night sky for you, one is AstroViewer, available for free (Only the online version is free, the downloadable version is not. But once you have opened the software, it doesn't require an internet connection any more).
A mini version of this software can be accessed from the left panel of this page. The full software can be started from this link AstroViewer night sky map . (It may need java update).
When you open the software, it would be somewhat like this:
Setting Your Own Location:
First you will have to customize the program. In the left hand panel of the software click on Location/City Tab. A box will appear like this:
For Pakistan, only coordinates of Karachi are present in the software, for any other place click on enter coordinates and enter the coordinates and name of the city:
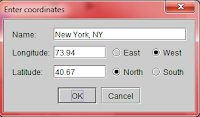
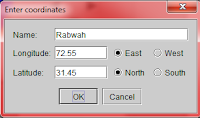
In relation to our blog, we have given the coordinates of Rabwah and Lahore in the left panel, for other places you will have to google the coordinates.
Once you enter the coordinates, the program shows the sky directly above you at that particular time. Confirm the time which is being shown in the left side of the program. If there is any difference from your local time, you will have to keep that in mind (for example when planning on seeing some object). I couldn't find any option to adjust the time to your local time.
Other Options:
Now that your location has been set, you can move the time backwards or forwards from the left bar below the location (or enter the date from calendar) and the software will immediately show the sky as it was or will be at the specified time and date. This comes in handy if you want to see what objects will be visible in the coming hours, days, months, or years. And when you click on the "now" tab, the sky swings back to that particular time.
How To Understand The Map:
Coming to the sky map now, it may look complicated with all kinds of dots and lines but in reality it is pretty simple.
The red circle is the whole of the sky above you. The center of the sphere is the zenith, the point exactly above your head. And so the area from the center of the sphere to the edge in any direction is the sky from directly above your head to the horizon in that particular direction.
The red dashed line crossing the circle is called "ecliptic". It is actually the path of the sun. Its importance is that moon and all the planets will always be at or near this line. This is so because all the planets in our solar system are revolving around the sun in the same plane.
How To Find Any Object From This Software In The Real Sky?
We will take the example of Venus for this. The yellow object on the left of the sun is Venus, (The program tells you all the details of any object when you right click on it. You can also search any object by name).
First of all activate the altitude scale from the left panel by clicking on it, a line will appear in the circle:
Now move the desired object (in this case Venus) on that line from the bottom scrolling button:
Now zoom the sky by moving the left scroll upwards. Then bring the object in view by moving the right scroll upwards:
Now you have to note two things from the program
1. Direction
2.Altitude
The direction of Venus in this case is slightly towards the northwest of west, and its altitude is between 45o and 50o. .
What this means is that you will have to face in this direction at this altitude to view the object.
How to Know The Direction?
The easiest and best way is to have a compass with you, (costs near Rs 100). But even if you don't have one you can estimate the directions fairly accurately both during daytime and night time.
If you know the direction in which sun sets everyday, that is West. The direction of horizon from where the sun rises is East. If East is on your right hand and West on your left, then your face is towards North and your back towards South.
During the night time, directions are pretty easy if you can find the North Star which is quite easy and will be discussed in a future post.
What remains is "Boxing the Compass". This is the further division between North, South, East and West e.g in between North and West is Northwest, and in between Northwest and North is 'North Northwest'. Following diagram explains this..
How to Know The Altitude?
At any time, the sky directly above your head, the zenith, is 90o.
The horizon (where earth and sky seem to be meeting) is 0o.
Midway between the two is 45o and so on.
Are All The Objects Shown in The Software Visible?
Although most will be visible on a clear night sky, it isn't that simple. The requirements for any object to be viewable are:
1) It should be night time. If an object is passing through your sky during the day, you cant view it because of the sunlight.
2) For planets, Elongation should be more than 15o. For the distant planets i.e Uranus and Neptune it should be more than 20o. (Elongation is the angle which a planet makes from the sun as viewed from the earth)
3) Altitude of any object, be it a star or a planet should be more than 10o, otherwise it is almost impossible to see.
4) Last and perhaps the most important are the Atmospheric conditions and Light Pollution. If atmospheric conditions are bad such as clouds or increased humidity then visibility will be low. Similarly light pollution in cities is a big problem, the city lights bounce back from the atmosphere and produce an orange hue in the sky severely hampering the visibility.
So don't expect to see a lot of things in a city for example Lahore, but in towns and countryside visibility should be pretty good, e.g in Rabwah.
5) Apparent magnitude(mag):
It is the relative brightness of the object as perceived by an observer on earth in perfect viewing conditions. The scale goes from negative to positive i.e. brighter the object lower is its apparent magnitude. For example Venus the brightest object (excluding the moon and the sun) has an apparent magnitude (mag) of -4.48 as compared to Mars which has a mag. of 0.23. An eye with normal vision is able to perceive objects of upto +6 in magnitude. The brightest star in the sky (of course after the sun) is Sirius (8.6 light years) with a mag of -1.4 whereas the Andromeda galaxy (2.2 million Light years) has a mag of 4.5
There are many other useful options in this software which will become apparent with further use.
There are a lot of software available online which plot the night sky for you, one is AstroViewer, available for free (Only the online version is free, the downloadable version is not. But once you have opened the software, it doesn't require an internet connection any more).
A mini version of this software can be accessed from the left panel of this page. The full software can be started from this link AstroViewer night sky map . (It may need java update).
When you open the software, it would be somewhat like this:
Setting Your Own Location:
First you will have to customize the program. In the left hand panel of the software click on Location/City Tab. A box will appear like this:
For Pakistan, only coordinates of Karachi are present in the software, for any other place click on enter coordinates and enter the coordinates and name of the city:


In relation to our blog, we have given the coordinates of Rabwah and Lahore in the left panel, for other places you will have to google the coordinates.
Once you enter the coordinates, the program shows the sky directly above you at that particular time. Confirm the time which is being shown in the left side of the program. If there is any difference from your local time, you will have to keep that in mind (for example when planning on seeing some object). I couldn't find any option to adjust the time to your local time.
Other Options:
Now that your location has been set, you can move the time backwards or forwards from the left bar below the location (or enter the date from calendar) and the software will immediately show the sky as it was or will be at the specified time and date. This comes in handy if you want to see what objects will be visible in the coming hours, days, months, or years. And when you click on the "now" tab, the sky swings back to that particular time.
How To Understand The Map:
Coming to the sky map now, it may look complicated with all kinds of dots and lines but in reality it is pretty simple.
The red circle is the whole of the sky above you. The center of the sphere is the zenith, the point exactly above your head. And so the area from the center of the sphere to the edge in any direction is the sky from directly above your head to the horizon in that particular direction.
The red dashed line crossing the circle is called "ecliptic". It is actually the path of the sun. Its importance is that moon and all the planets will always be at or near this line. This is so because all the planets in our solar system are revolving around the sun in the same plane.
How To Find Any Object From This Software In The Real Sky?
We will take the example of Venus for this. The yellow object on the left of the sun is Venus, (The program tells you all the details of any object when you right click on it. You can also search any object by name).
First of all activate the altitude scale from the left panel by clicking on it, a line will appear in the circle:
Now move the desired object (in this case Venus) on that line from the bottom scrolling button:
Now zoom the sky by moving the left scroll upwards. Then bring the object in view by moving the right scroll upwards:
Now you have to note two things from the program
1. Direction
2.Altitude
The direction of Venus in this case is slightly towards the northwest of west, and its altitude is between 45o and 50o. .
What this means is that you will have to face in this direction at this altitude to view the object.
How to Know The Direction?
The easiest and best way is to have a compass with you, (costs near Rs 100). But even if you don't have one you can estimate the directions fairly accurately both during daytime and night time.
If you know the direction in which sun sets everyday, that is West. The direction of horizon from where the sun rises is East. If East is on your right hand and West on your left, then your face is towards North and your back towards South.
During the night time, directions are pretty easy if you can find the North Star which is quite easy and will be discussed in a future post.
What remains is "Boxing the Compass". This is the further division between North, South, East and West e.g in between North and West is Northwest, and in between Northwest and North is 'North Northwest'. Following diagram explains this..
How to Know The Altitude?
At any time, the sky directly above your head, the zenith, is 90o.
The horizon (where earth and sky seem to be meeting) is 0o.
Midway between the two is 45o and so on.
Are All The Objects Shown in The Software Visible?
Although most will be visible on a clear night sky, it isn't that simple. The requirements for any object to be viewable are:
1) It should be night time. If an object is passing through your sky during the day, you cant view it because of the sunlight.
2) For planets, Elongation should be more than 15o. For the distant planets i.e Uranus and Neptune it should be more than 20o. (Elongation is the angle which a planet makes from the sun as viewed from the earth)
3) Altitude of any object, be it a star or a planet should be more than 10o, otherwise it is almost impossible to see.
4) Last and perhaps the most important are the Atmospheric conditions and Light Pollution. If atmospheric conditions are bad such as clouds or increased humidity then visibility will be low. Similarly light pollution in cities is a big problem, the city lights bounce back from the atmosphere and produce an orange hue in the sky severely hampering the visibility.
So don't expect to see a lot of things in a city for example Lahore, but in towns and countryside visibility should be pretty good, e.g in Rabwah.
5) Apparent magnitude(mag):
It is the relative brightness of the object as perceived by an observer on earth in perfect viewing conditions. The scale goes from negative to positive i.e. brighter the object lower is its apparent magnitude. For example Venus the brightest object (excluding the moon and the sun) has an apparent magnitude (mag) of -4.48 as compared to Mars which has a mag. of 0.23. An eye with normal vision is able to perceive objects of upto +6 in magnitude. The brightest star in the sky (of course after the sun) is Sirius (8.6 light years) with a mag of -1.4 whereas the Andromeda galaxy (2.2 million Light years) has a mag of 4.5
There are many other useful options in this software which will become apparent with further use.









I am now at Nazarat-Taleem until 4 October, thereafter I will return in December 2016. I would like to contact an amateur astronomer in Rabwah to run some experiments on the sounds carried by the flickering visible light emitted from the black hole V404 Cygni. If someone is interested, you can email thomas.prevenslik@gmail.com
ReplyDelete